 In this book, we will be using HTML, JavaScript, and CSS3 to program the front end. The front end, also known as the browser side, is what you see in your web browser when you visit a website.
In this book, we will be using HTML, JavaScript, and CSS3 to program the front end. The front end, also known as the browser side, is what you see in your web browser when you visit a website.
It's important to put the same amount of effort into the front
end as it is the layer of the web application that users interact with, and it should convey the right message to the end user.
If a user visits a website with an unfriendly user interface (UI), they may leave, which can be costly to any business. As a Software Developer, prioritizing user experience should always be a priority, as users are the center of any application.
Here's a step-by-step outline for creating the front end of a social media application using ASP.NET Core:
Step 1: Set up ASP.NET Core Project
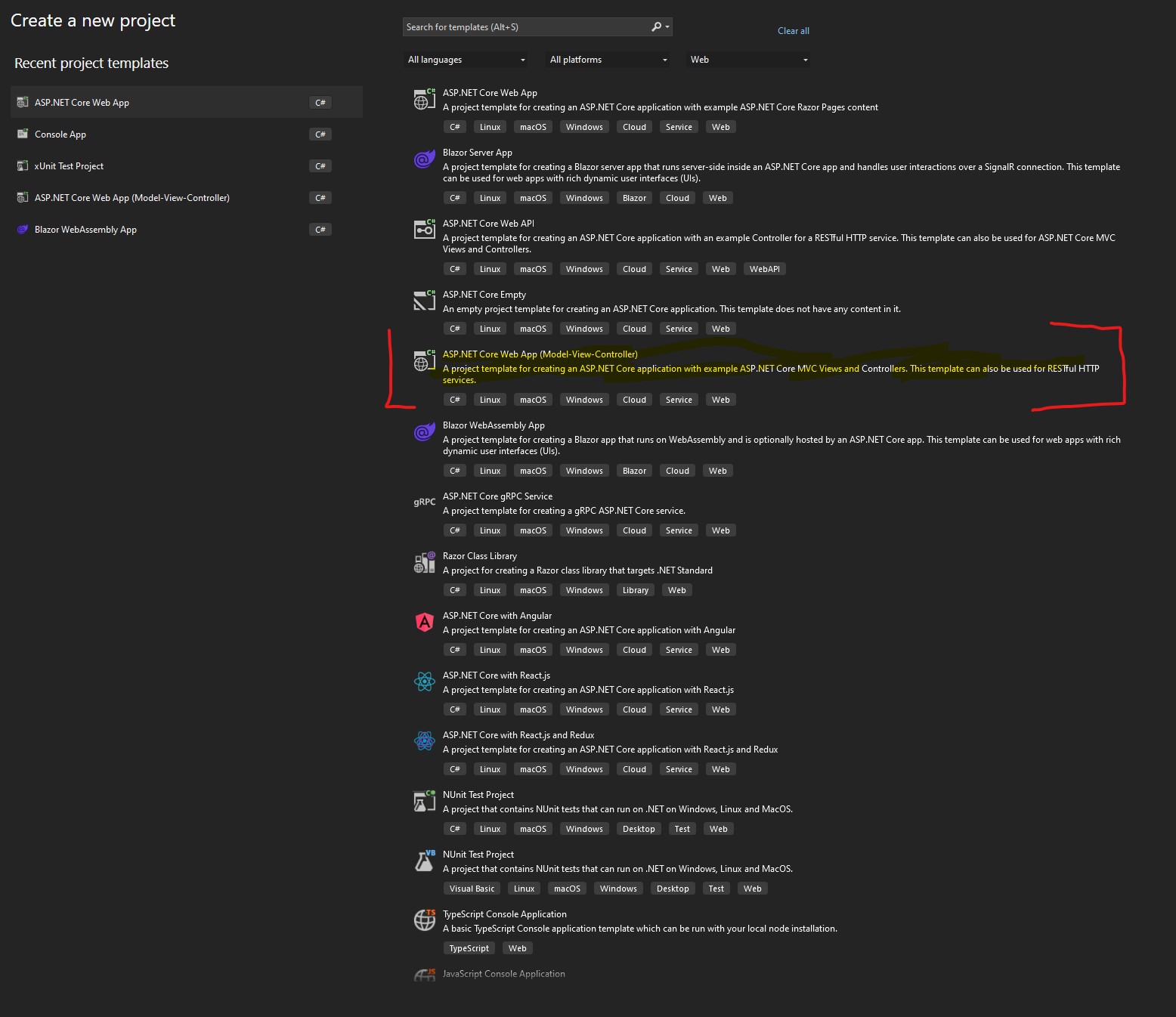
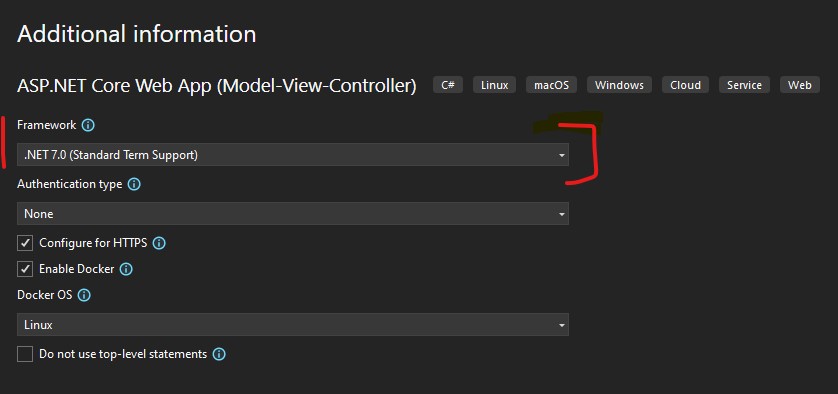
Step 2: Design the User Interface
4. Define the overall layout and design of your social media application, including the home
page, login/register pages, user profile pages, timeline/feed pages, and other relevant pages.

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>@ViewData["Title"] - MyFaceSocialMedia</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="~/css/site.css" asp-append-version="true" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="~/MyFaceSocialMedia.styles.css" asp-append-version="true" />
</head>
<body>
<header>
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-sm navbar-toggleable-sm navbar-light
bg-white border-bottom box-shadow mb-3">
<div class="container-fluid">
<a class="navbar-brand" asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Index">MyFaceSocialMedia</a>
<button class="navbar-toggler" type="button" data-bs-toggle="collapse"
data-bs-target=".navbar-collapse" aria-controls="navbarSupportedContent"
aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<div class="navbar-collapse collapse d-sm-inline-flex justify-content-between">
<ul class="navbar-nav flex-grow-1">
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link text-dark" asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Index">Home</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link text-dark" asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Privacy">Privacy</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</nav>
</header>
<div class="container">
<main role="main" class="pb-3">
@RenderBody()
</main>
</div>
<footer class="border-top footer text-muted">
<div class="container">
© 2023 - MyFaceSocialMedia -
<a asp-area="" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="Privacy">Privacy</a>
</div>
</footer>
<script src="~/lib/jquery/dist/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script src="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"></script>
<script src="~/js/site.js" asp-append-version="true"></script>
@await RenderSectionAsync("Scripts", required: false)
</body>
</html>
The code above is an HTML file that represents the layout of a web page. It starts with the <!DOCTYPE html> declaration, which specifies the version of HTML being used.
The <html> tag encloses the entire document, and the lang attribute indicates that the language of the document is English.
The <head> tag contains information about the document, such as the title, character set, and any external stylesheets or scripts that should be loaded.
The <meta> tags specify the character set and viewport of the document. The title element sets the title of the web page, which is dynamically generated using the @ViewData["Title"] expression.
The <link> tags import stylesheets from the bootstrap.min.css, site.css, and MyFaceSocialMedia.styles.css files. These stylesheets define the layout, typography, and other visual elements of the web page.
The <body> tag encloses the content of the web page, which includes a navigation bar defined by the <nav> tag and a header element defined by the <header> tag.
The <main> tag contains the main content of the page, which is dynamically generated using the @RenderBody() expression.
Finally, the <footer> tag defines the footer element of the page, which includes a copyright notice and a link to the privacy policy. The <script> tags load external JavaScript files, including the jQuery library and the site.js file, which provides custom scripts for the web page.
The @await RenderSectionAsync("Scripts", required: false) expression is used to dynamically render any additional scripts that may be defined in the view.
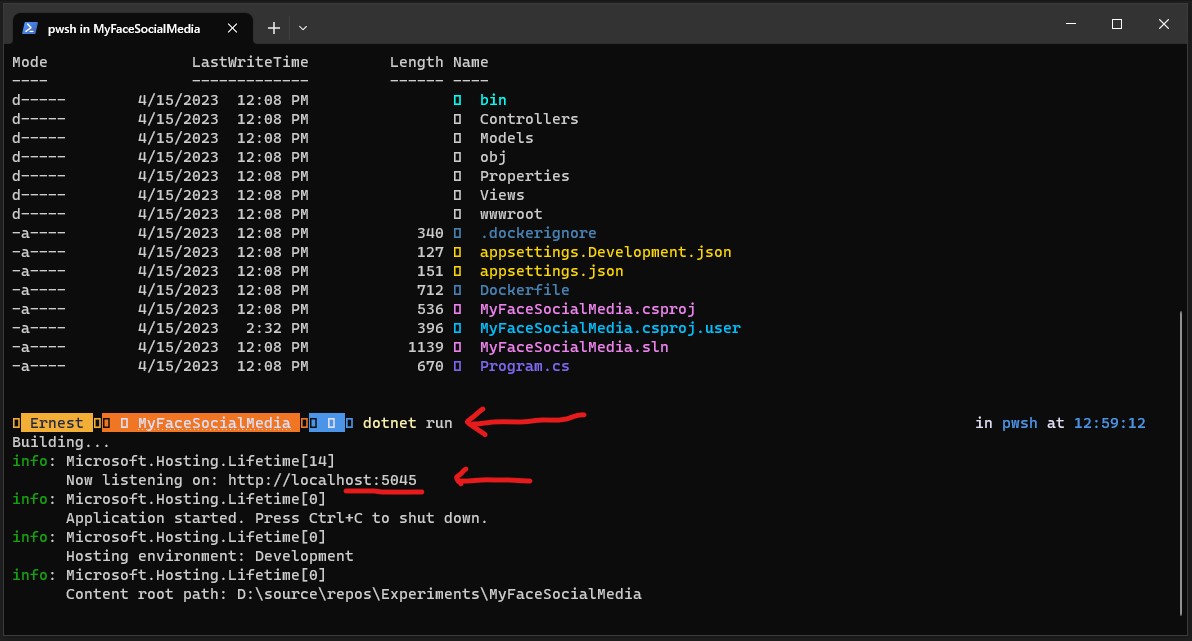
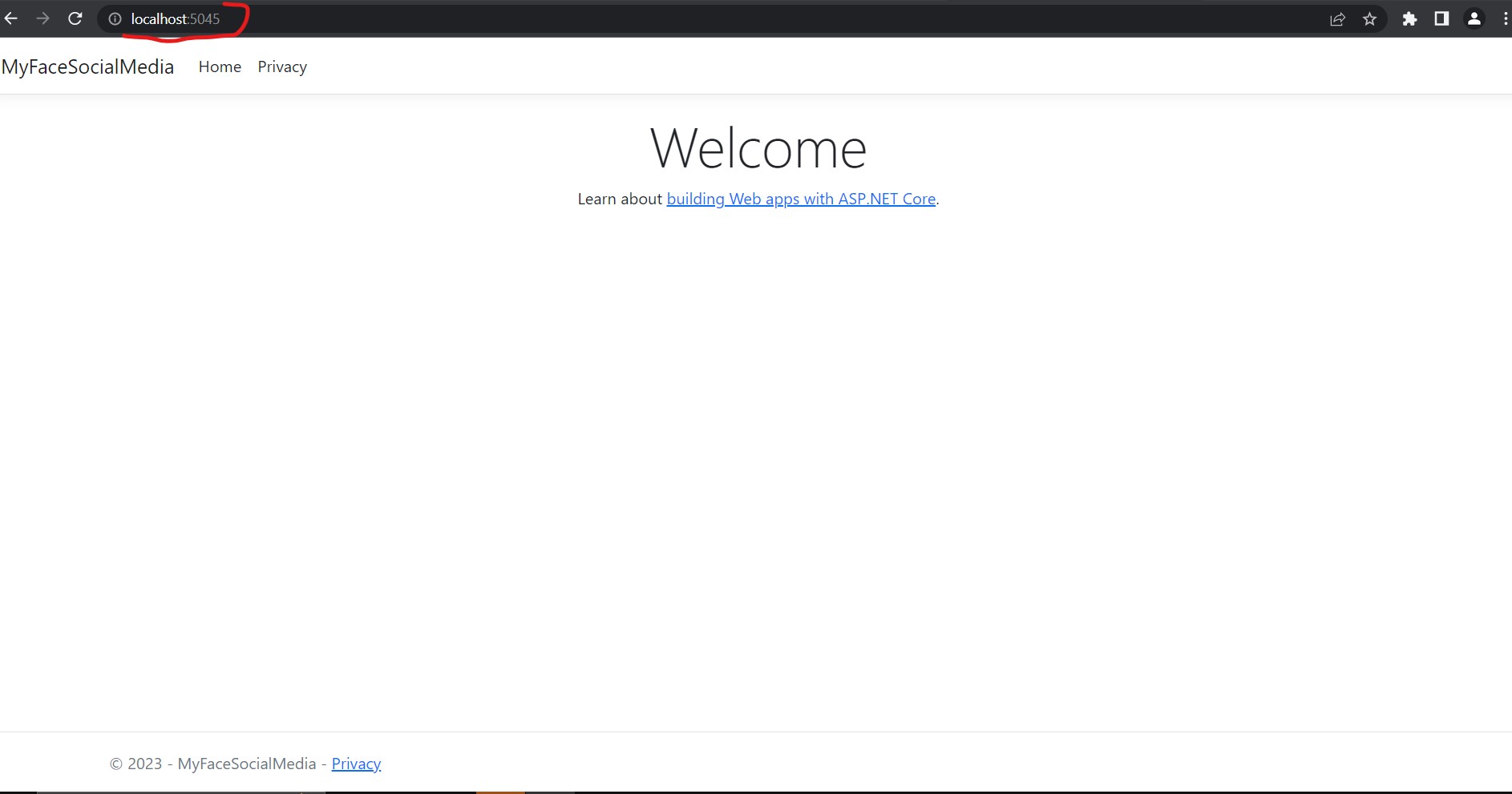
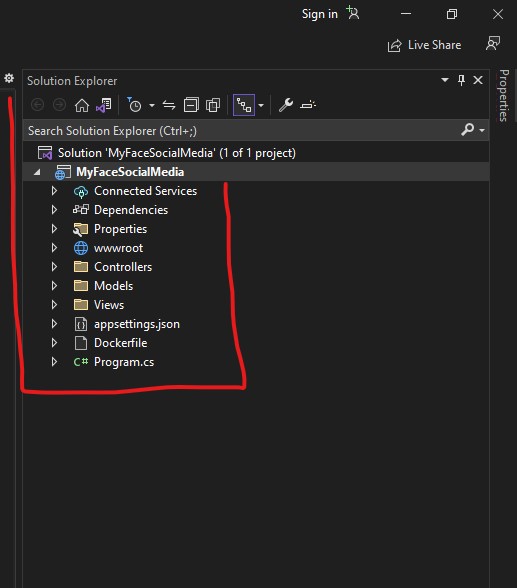
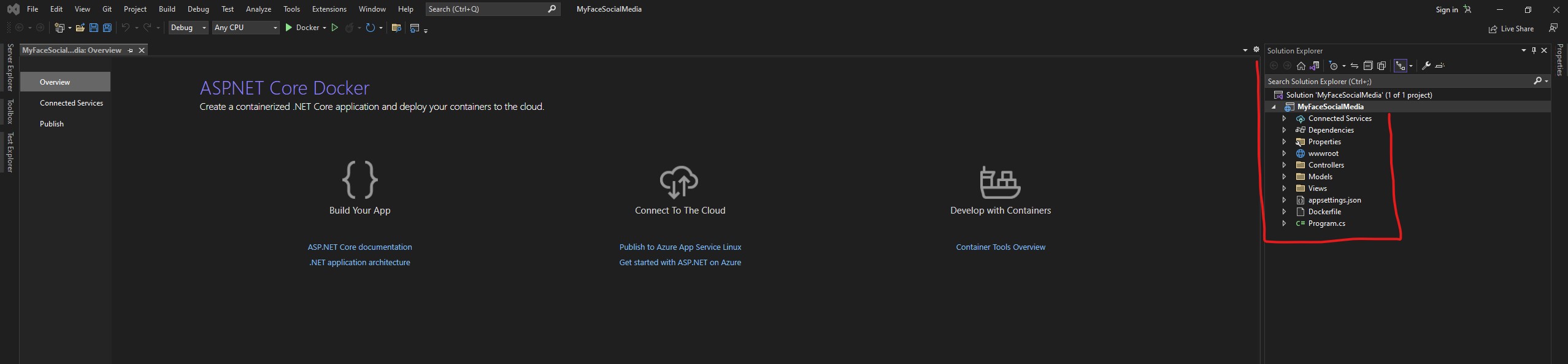
Controllers: This folder contains the controllers, which are responsible for processing incoming HTTP requests and generating HTTP responses. Controllers handle the business logic and define the behavior of different routes and endpoints in the web application.
Views: This folder contains the views, which are responsible for rendering the user interface. Views are typically written in HTML with embedded code using Razor syntax, which allows for dynamic content generation.
Models: This folder contains the models, which are responsible for defining the data entities and data access logic for the web application. Models represent the data and business objects used by the application.
wwwroot: This folder is the root folder for static files, such as CSS, JavaScript, and images. Static files are served directly by the web server without going through the MVC pipeline, making them efficient for serving static content.
Data: In some cases, a Developer might want to include a Data folder, which may contain data-related components, such as database models, data context, and data access logic. It's common to use a separate folder for organizing data-related components in a structured manner.
Middleware: This folder may contain custom middleware components that can handle cross-cutting concerns, such as authentication, logging, or caching. Middleware components are executed in the order they are registered in the pipeline and can intercept and process HTTP requests and responses.
Configuration: This folder may contain configuration files, such as appsettings.json, which store various configuration settings for the application, such as database connection strings, logging settings, and app-specific configurations.
Areas: This folder may contain subfolders representing different areas of the application, which are used for organizing related components, such as views, controllers, and models, in a modular manner.
Startup.cs: This file contains the configuration for the application's startup, including configuring services, middleware, and other settings.
Other folders: Depending on the requirements of the application, there may be additional folders for organizing specific components, such as Services, Helpers, Utilities, or Tests
- Make sure required folders are thought of and included in the overall Software design.
Step 3: Implement Views
7. Implement views for each page of your social media application using Razor views,
which allows you to combine HTML markup with C# code to generate
dynamic content.
Step 4: Implement Models.
Define data models that represent the entities in your social media
application, such as users, posts, comments, and other relevant data.
Step 5: Implement Controllers
12. Create controllers that handle HTTP requests from your views and interact with your models to
fetch and update data.
Step 6: Implement Client-Side Interactions
15. Use JavaScript and relevant libraries/frameworks, such as jQuery, to implement
client-side interactions, such as dynamic content updates, form submissions, and other
user interactions.
Step 7: Test and Debug
17. Test your social media application by manually verifying different scenarios, such as user
registration and login, posting and viewing posts, commenting, and other functionalities.
Step 8: Optimize and Refactor
19. Optimize your front-end code for performance, security, and accessibility.
This is a general outline for creating the front end of a social media application using ASP.NET Core. The actual implementation in many production Sites may vary depending on specific application requirements, chosen technologies, and design patterns. It's important to follow best practices, maintain security measures, and thoroughly test your application to ensure its reliability and user-friendliness.